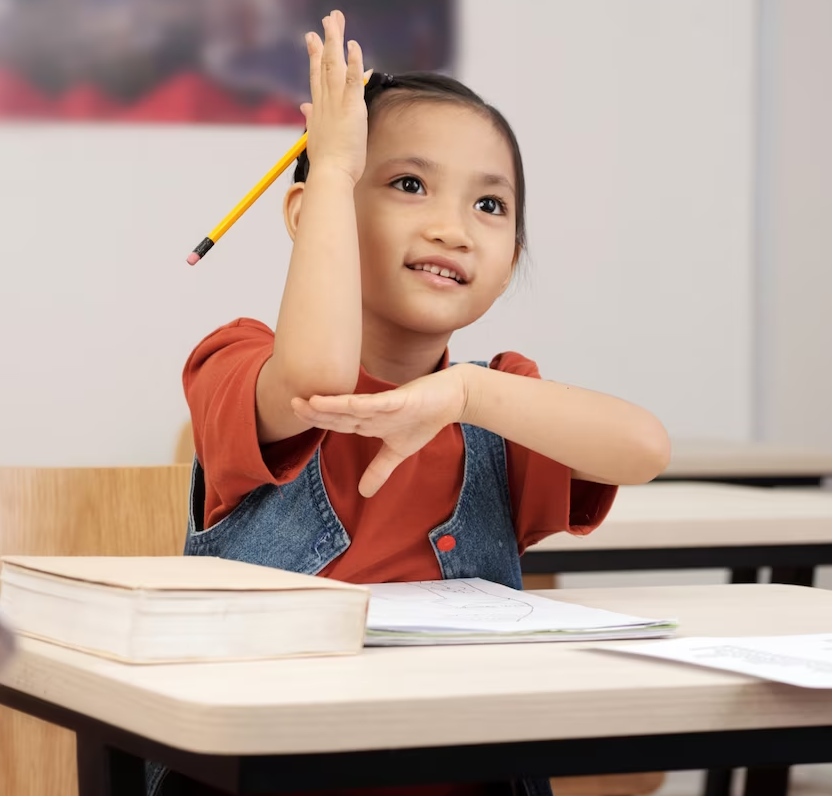
We developed an outcome-oriented methodology designed to achieve success.
Menu
- Home
- About Us
- Our ProgramsMenuMenu
- Resources
- Contact Us
- Home
- About Us
- Our ProgramsMenuMenu
- Resources
- Contact Us
Enjoy up to 4 lessons off when you enrol today FIND OUT MORE
OUR METHOD
Just like a computer, the brain needs proper programming to function optimally. Brain training achieves this by exercising cognitive skills, similar to how physical fitness strengthens the body. This involves activities or games designed to maintain or enhance cognitive abilities, whether through interactive games, scheduled cognitive tasks, or visuospatial challenges.
TRANSFORMING BRAIN TRAINING INTO ACADEMIC EXCELLENCE

Cognitive Boost
Our SMARTWAVE program strengthens your child's cognitive foundation, enhancing their capacity.
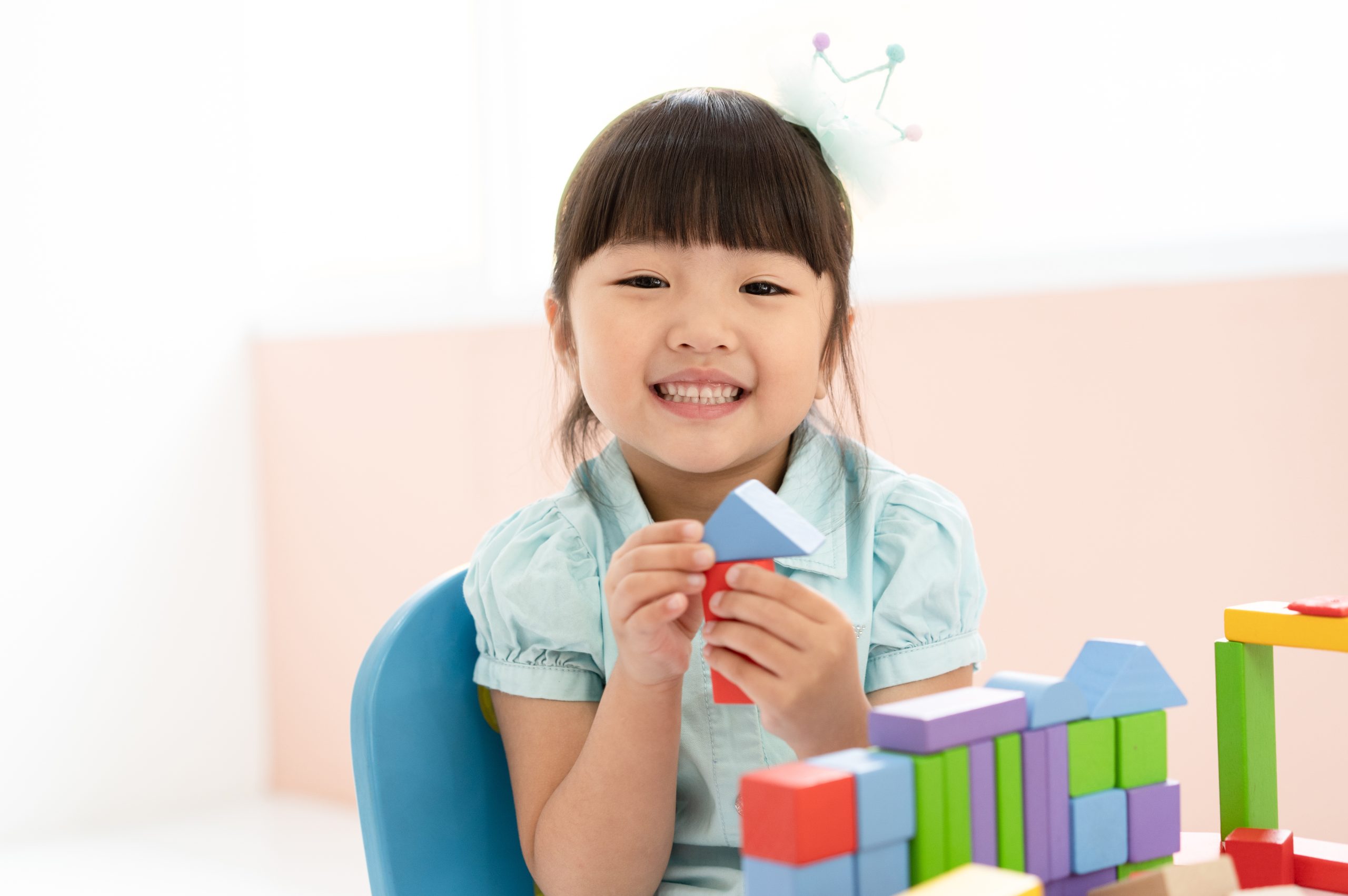

Intellectual Growth
Our journey continues with the Intellectual Thinking Ability Program, refining and elevating our students' intellectual capacities.
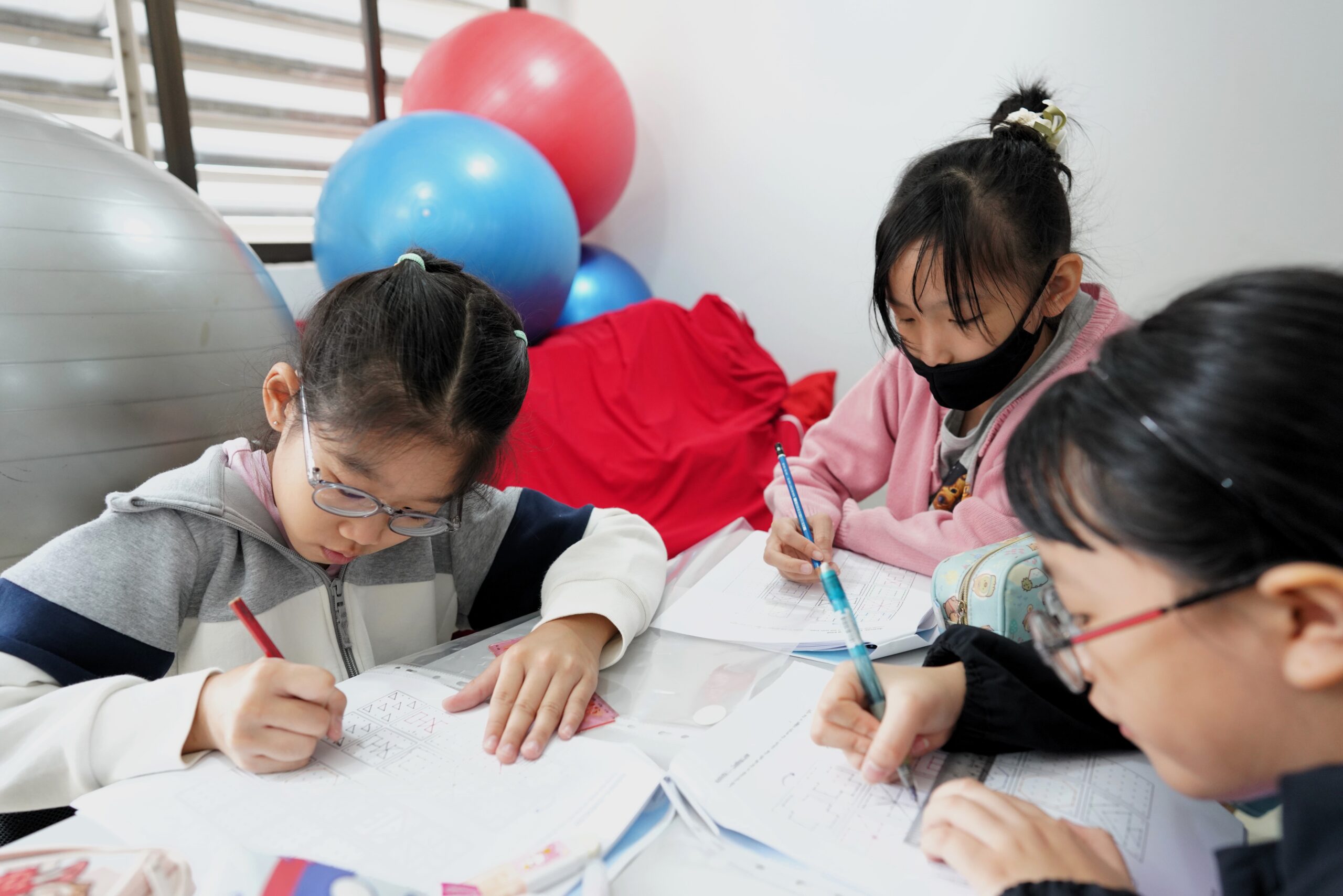

Academic Advancement
Transition into our English and Math Academy's curriculum, where your child can excel further in their subjects.

Academic Excellence
Academic excellence is achieved by mastering subjects through enhanced cognitive ability, empowering your child to reach their full potential.
SMARTWAVE Model
SMARTWAVE MODEL
S Speed in Processing
Speed in handling simple mental tasks in a reasonable time frame
M Mindset Shaping
Mental attitude towards motivated improvement of self at school and in life
A Attention and Focus
Ability to filter out internal and external distractions by selecting only the information required for the task
R Reasoning with Logic
Ability to form concepts, logic and relationships with unfamiliar information
T Time and Rhythm
The rhythm in communicating and executing daily activities in a timely manner
W Working Memory
Ability to hold and retrieve information while performing a mental task
A Auditory Analysis
Ability to store, analyse and manipulate sounds crucial for reading and spelling
V Visual Processing
Ability to identify, discriminate and manipulate visual information
E Emotional Control
Modulation of stimuli and regulation of emotional state to remain calm and clear headed

The Brain Academia’s holistic cognitive training approach focuses on addressing 9 cognitive blocks (S.M.A.R.T.W.A.V.E) which serves as the foundation for brain fitness by increasing processing Speed, shaping Mindset, strengthening Attention, enhancing Reasoning, cultivating Time & rhythm, improving Working memory, reinforcing Auditory analysis, fortifying Visual processing, and managing Emotions. Integrated with our Intellectual Thinking Abilities Program (INTAP), students develop abstract thinking skills, enabling them to approach problems with creative solutions using memory, symbolic relationships, semantic connections, and critical assessment.
COGNITIVE SKILLS & Mindset
INTELLECTUAL Thinking Abilities
ACADEMIC Focus & Learning
ACHIEVING
SUCCESS!
INTELLECTUAL Thinking Abilities

ACHIEVING
SUCCESS!
Embedded within all our programs, the SMARTWAVE formula ensures that students can anticipate these advantages when engaging with academic content in school.
- Ease in forming connections in academic reading materials.
- Ability to hold and sequence subject data or information.
- Ability to hold information presented verbally by teachers and peers.
- Improvement in spelling and visual concentration.
- Stronger ability to retain unrelated facts till some form of connection is achieved.
- Ability to conceptualise modern math approaches and set concepts.
- Stronger memory for details and sequencing.
- Reduced math anxiety due to inability to handle ambiguity.
- Minimise issues with similarities and differences.
- Better hand and eye coordination
- Improved visual judgements.
- Careful and organized with details.
- Ability to use sound reasoning and logic.
- Better command of arithmetic processes
- Faster data browsing or scanning ability.
- Enhanced ability to produce and put together ideas.
- Confident and willingness to explore problem solving solutions.